Question & Answer
Question
How does QRadar HA peers replicate data between Cluster nodes?
Answer
QRadar High Availability (HA) nodes work on an Active and Standby model. When the Primary/Active node goes offline the Secondary/Standby node switches to Active. HA uses two methods to keep QRadar data synchronized and all files updated by sending data from the Active node to the Standby node by using Distributed Replicated Block Device (DRBD) and Rsync. DRBD works at the block level, which keeps
/store up to date on the Secondary/Standby node. Rsync keeps all other facets of QRadar up to date including the updated Protocols, DSMs, and configuration files. QRadar uses Crossover connections to move the data to the Secondary/Standby node to reduce traffic from the management interface. DRBD is started before the HA Manager. HA Manager still controls the flow of the data and looks at the last good state of the HA Cluster, when started it determines who is the current good Active node. HA Manager verifies that all data is current on the Standby node and updates accordingly.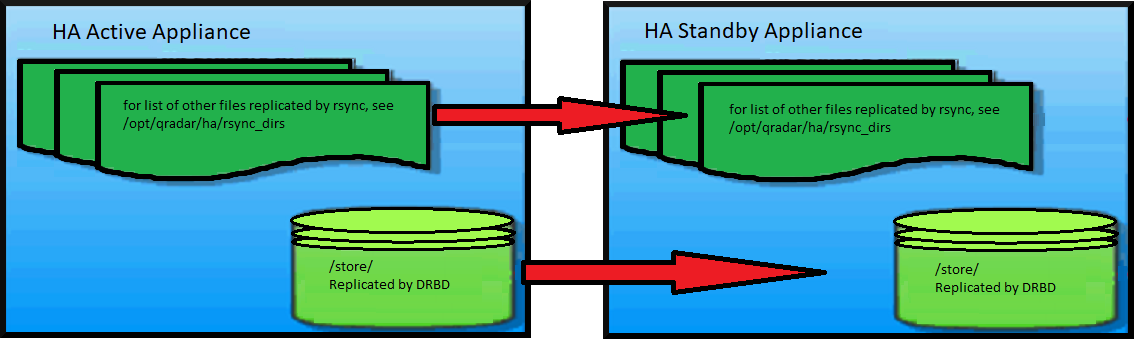
Related Information
[{"Type":"MASTER","Line of Business":{"code":"LOB24","label":"Security Software"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU059","label":"IBM Software w\/o TPS"},"Product":{"code":"SSBQAC","label":"IBM Security QRadar SIEM"},"ARM Category":[{"code":"a8m0z000000cwtXAAQ","label":"High Availability"}],"ARM Case Number":"","Platform":[{"code":"PF016","label":"Linux"}],"Version":"7.4.0;7.4.1;7.4.2;7.4.3;7.5.0"}]
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
24 July 2023
UID
swg21993804