Troubleshooting
Problem
Handle heap is a type of temporary storage that an application and the operating system use. This document describes how to use the system service tools macro HANDLEHEAPS output to determine the jobs that own the largest handle heap and the current sizes. This support can also be used to monitor for growth of the heaps. If the heap fills, this will result in MCH6903 F/#hmalcmi with an activation group mark that is zero . See the following reference for additional details on this type of heap: Single Level Storage Heap
Resolving The Problem
Use these steps to collect and review the HANDLEHEAPS macro output from system service tools:
STEP 1: Collect the output:
- STRSST <enter>
- Specify credentials <enter>
- 1. Start a service tool <enter>
- 4. Display/Alter/Dump <enter>
- 2. Dump to printer <enter>
- 2. Licensed Internal Code (LIC) data <enter>
- 14. Advanced analysis <enter>
- Specify an option of 1 and the command HANDLEHEAPS <enter>
- Specify options of -s <enter>
- Specify a dump title <enter>
- Exit system service tools by pressing F3 <exit> and watch for one of these messages:
If the following message appears, then take option 7. Display dump status and wait until the dump completes.
Dumps still incomplete. Press F3=Exit or F12=Cancel to end.
If the following message appears, then continue to press F3 <exit> and <enter> to exit System Service Tools
Dump completed normally -SAMPLE 1
STEP 2: Review the output:
- WRKJOB OPTION(*SPLF) <enter>
- Locate the spooled file named QPCSMPRT and take option 5=Display <enter>
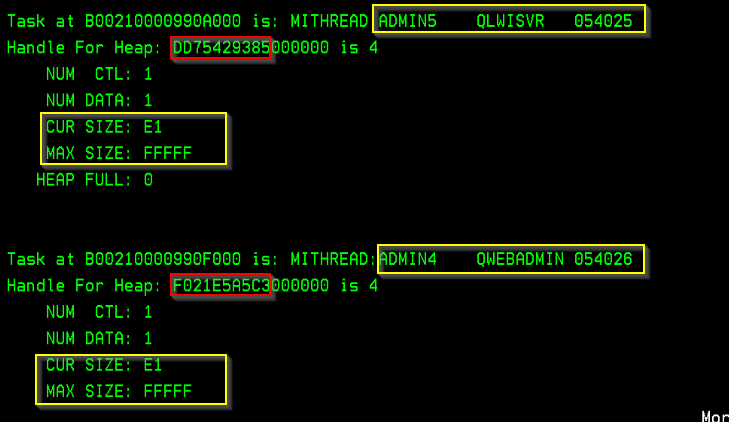
Refer to the example below for sample output.
- The output lists the heaps and the owning jobs in descending order by CUR SIZE (current size).
- A typical failure when a specific heap fills is MCH6903 in the given job owning the heap. Restarting the job is typically all that is required to recover.
- This example shows two heaps, the first one owned by job 054025/QLWISVR and the second one owned by job 054026/QWEBADMIN/ADMIN4.
- The first heap owned by job 054025 has a current size of x'E1' pages out of the maximum size of x'FFFFF'. The second heap owned by job 054026 has a current size of x'E1' pages out of maximum size of x'FFFFF'
- A page is 4096 byes.
- The CUR SIZE (current size) should typically reach some peak value and remain. If the CUR SIZE continues to increase until the job eventually fails with an error, like MCH6903 F/#hmalcmi , then this implies a leak.
- Multiple HANDLEHEAPS -s can be taken over time to determine if a heap continues to grow.
- 'DD75429385' and 'F021E5A5C3' are examples of the address that uniquely identify the heap. Some advanced PEX traces use a filter and this value will be required to uniquely identify the heap.
[{"Type":"MASTER","Line of Business":{"code":"LOB57","label":"Power"},"Business Unit":{"code":"BU058","label":"IBM Infrastructure w\/TPS"},"Product":{"code":"SWG60","label":"IBM i"},"ARM Category":[{"code":"a8m0z0000000CGHAA2","label":"MustGather"}],"ARM Case Number":"","Platform":[{"code":"PF012","label":"IBM i"}],"Version":"All Versions"}]
Historical Number
587269612
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
05 March 2024
UID
ibm16557454