Troubleshooting
Problem
Environment
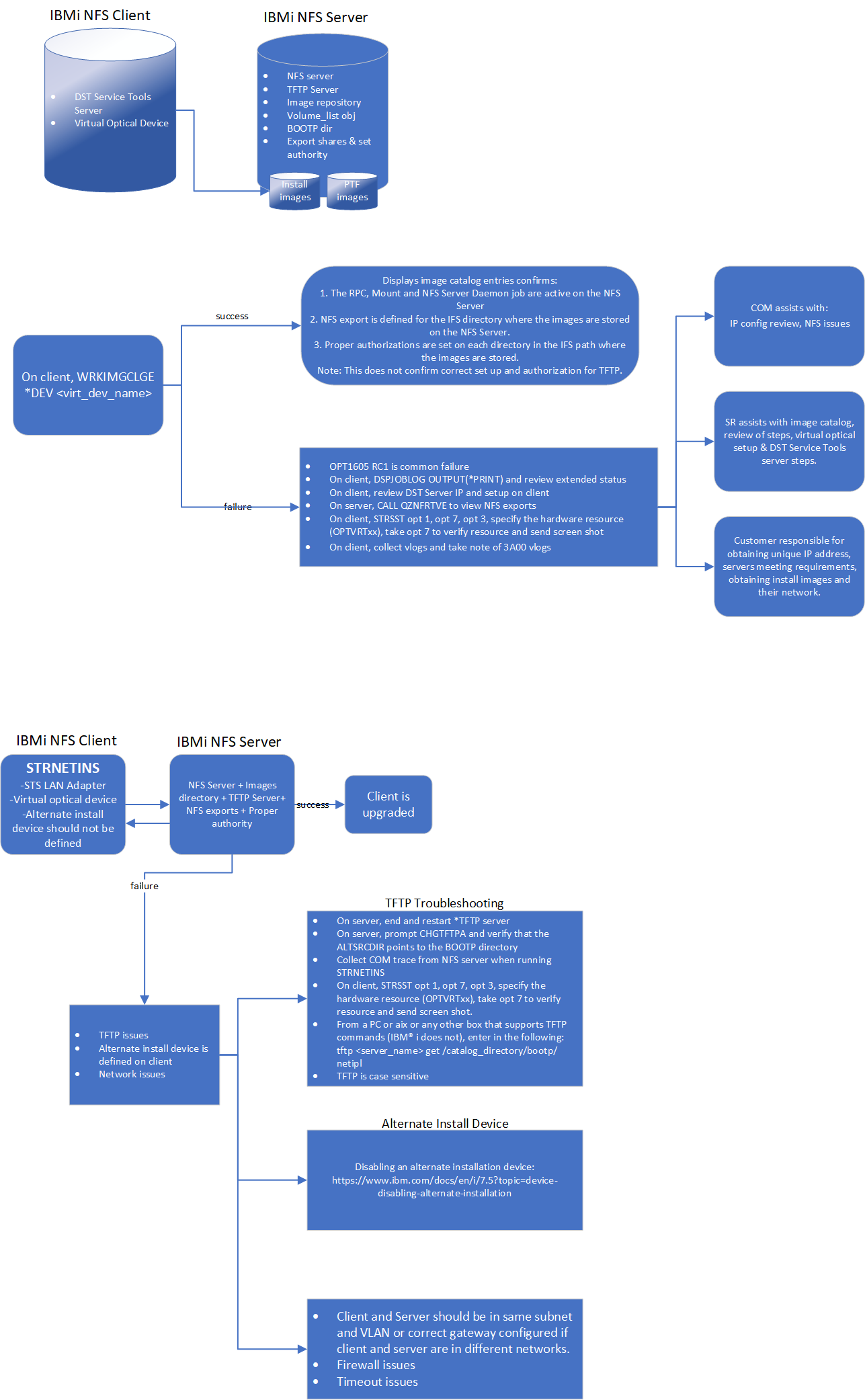
Diagnosing The Problem
- CFGTCP -> 1 -> F6
- CFGTCP -> 2 -> F6
- CFGTCP -> 10 -> F6
- CFGTCP -> 12 -> take a snapshot
- WRKCFGSTS CFGTYPE(*LIN) CFGD(*ELAN) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- Snapshot of CHGTFTPA -> note the alternate source directory name
- Snapshot of WRKIMGCLGE IMGCLG(<image_catalog_name>)
- DSPLIND OUTPUT(*PRINT) of the Ethernet line description that is associated to the XPF TCP/IP interface they are trying to use on the Server
- WRKACTJOB OUTPUT(*PRINT) JOB(QNF*)
- WRKACTJOB OUTPUT(*PRINT) JOB(QTTFT*)
- DSPPTF OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- WRKPTFGRP, F6 + ENTER /* this generates a spooled file */
- DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*AHW) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- DSPFMWSTS OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- CALL QZNFRTVE /*lists directories exported and version of NFS*/ Then run DSPJOBLOG OUTPUT(*PRINT) and send joblog.
- Communications trace if client lpar halts after STRNETINS is attempted.
From the Client (Network Upgrade):
- CFGTCP -> 1 -> F6
- CFGTCP -> 2 -> F6
- CFGTCP -> 10 -> F6
- CFGTCP -> 12 -> take a snapshot
- DST/SST LAN Adapter snapshot:
- STRSST -> 8 -> F5
- WRKCFGSTS CFGTYPE(*LIN) CFGD(*ELAN) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- DSPLIND OUTPUT(*PRINT) of the Ethernet line description that is associated to the TCP/IP interface they are trying to use on the Client
- DSPPTF OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- WRKPTFGRP, F6 + ENTER /* this generates a spooled file */
- DSPHDWRSC TYPE(*AHW) OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- DSPFMWSTS OUTPUT(*PRINT)
- PRTINTDTA TYPE(*DMP) DMPID(*ALL) /* take note of 3A00 vlogs when logging optical errors */
Determine the hardware resource associated with the NFS backed optical device. Then, issue STRSST opt 1, opt 7, opt 3, specify the hardware resource (OPTVRTxx), take opt 7 to verify resource and send screen shot of the ‘Removable Media Hardware Verification’ screen.
A majority of the documentation that is requested for the client and server LPARs, can be collected with a SYSSNAP. To collect data via SYSSNAP:
1 - Install QMGTOOLS on both LPARS with instructions from the following technical document:
https://www.ibm.com/support/pages/mustgather-how-obtain-and-install-qmgtools-and-keep-it-current
2 - Collect System Snapshot that uses the following CL command on both LPARs:
QMGTOOLS/SYSSNAP OUTPUT(*IFS) COLLECTDFT(Y) LICLOGS(Y) PALS(Y) QHST(Y/Y) DAYSPRV(*DATE) STRDATE(mmddyy) ENDDATE(mmddyy)
From the NFS Server LPAR:
- Snapshot of CHGTFTPA
- Snapshot of WRKIMGCLGE IMGCLG(<image_catalog_name>)
- Communications trace if client lpar halts after STRNETINS is attempted.
From the Client LPAR:
- DST/SST LAN Adapter snapshot: STRSST -> 8 -> F5
- Determine the hardware resource associated with the NFS backed optical device. Then, issue STRSST opt 1, opt 7, opt 3, specify the hardware resource (OPTVRTxx), take opt 7 to verify resource and send screen shot of the ‘Removable Media Hardware Verification’ screen.
Resolving The Problem
• System must be at IBM® i 6.1 or greater.
• IBM® i 6.1 PTF’s SI57013 and SI44484.
• IBM® i 7.1 PTF’s SI59835
2. The image server must reside on a supported IBM i version if performing an installation or upgrade.
3. The server must be able to share virtual optical images that use version 3 or later of the Network File System (NFS).
4. A volume list (VOLUME_LIST) file that contains the list of images to be loaded in the virtual optical device must exist in the image catalog directory. The VFYIMGCLG command is used to create the volume list file from the image catalog that contains the images you want to share. For example,:
VFYIMGCLG IMGCLG(INSTALL) TYPE(*UPGRADE) NFSSHR(*YES)
– Must be called VOLUME_LIST
– Each line is either an image file name or a comment
– ASCII format
– All entries are ended by the end of a line
– All characters that follow the pound sign (#) are considered comments until the end of the line
– Comments can be added after the pound sign (#) and must be followed by a EOL character
– Provides the order that the image files are processed on the client system
– File names are limited to 127 characters
– Can be created with the Verify Image Catalog Entry (VFYIMGCLG) with the NFSSHR(*YES) parameter or manually by using an ASCII editor
– No tabs or line feeds can be used in the path name
• The 632B-003 optical device is created by using the Create Device Description Optical (CRTDEVOPT) command.
• The system to be installed must have either a service tools server or a LAN console connection configured.
Target (Client) PTF requirements if Client is older than IBM i 7.2:
• IBM® i 6.1 PTFs SI39400 (Lead PTF – this ptf causes the other PTFs to be ordered and installed), SI57013, SI44484, SI35747, MF50920, and MF47285
• IBM® i 7.1 PTF SI59835
• Only supported by Hardware Management Console (HMC) 7.2 or later
• Power 6 EFW Service Pack 3.5.5, 10/21/2010 or later
• Power 7 EFW 7.2 or EFW 7.1 with Service Pack 7.1.4, 09/22/2010 or later
(Supports stand-alone PCI Ethernet adapters only)
• Power 7 EFW 7.3 with service pack 7.3.3, 09/14/2011 or later (Supports stand-alone PCI Ethernet adapters and virtual ethernet adapters)
- This command displays the "Work with Image Catalog Entries" panel that shows a catalog of type *RMTCLG and showing all the volumes. If all the volumes are displayed, this output means the prep work on the server of ensuring NFS servers were running, exporting the correct directory, and proper authorizations of the catalog directory contents.
- If errors, DSPJOBLOG OUTPUT(*PRINT) for joblog.
- The main reasons WRKIMGCLGE fail are setup issues with either no VOLUME_LIST in the image catalog directory, not authorizing the objects in the image catalog directory properly, NFS is not up and running correctly (with the exported path) on the server, or the client's service Lan adapter is not activated with a valid IP address. Many times, WRKIMGCLG *DEV < virtual_device_name > posts message OPT1605 RC1.For message OPT1605 RC1, a good place to start is to redo the steps on the NFS server to VFYIMGLG, end and restart NFS servers, re-add proper authorities, reexport and then on the client system vary off/on the network-backed device.
- Message OPT1605 RC1 has an extended status for the error, which can be seen in the joblog. Here are the meanings of the last 2 bytes:
CFC2 - media list error
CFC3 - media list invalid
CFC4 - virtual volume access problem - includes not found
CFC5 - virtual volume read error
CFC6 - virtual volume invalid
CFC7 - virtual device problem
CFC8 - 632B-003 device problem
Error state meanings:
1 - NFS Time-out.
2 - NFS Permission denied.
3 - No such NFS path or directory.
4 - NFS connection rejected.
5 - NFS file system is read only.
40 - Incorrect NFS argument, Check proper ASCII/EBCDIC content.
90 - Unknown NFS State.
95 - Server does not respond to PING.
99 - NFS return code problem.
100 - VOLUME LIST invalid use of / in file name.
101 - VOLUME LIST line length exceeds 256 characters.
102- VOLUME LIST contains too many file names.
103 - VOLUME LIST file name contains W key, but then another nonblank character.
104 - VOLUME LIST has an unsupported character or an imbedded blank.
120 - VOLUME LIST problem, contact next level support.
199 - Error varying on the hardware driver. Check for PALs or VLOGs.
200 - Hardware driver is in Failed state.
300 - Hardware driver is in Software Error state.
Review DST Service Tools Setup and configuration:
- Prior to activating the DST Service Tools server, ensure that the IP address cannot be pinged. After activating the DST service tool server, verify that the IP address assigned can be pinged.
To activate:
a) Start System Service Tools (STRSST).
b) Work with service tools user IDs and Devices (Option 8).
c) Select STS LAN adapter (F13) to see available adapters. If you press F13 and there are no available adapters listed, press F21 to show all adapters. F13 will not show a resource with an active line description. You can share a resource that is being used on the system; however, the resource assigned to the STS Lan adapter cannot be active on the system. You have to end the interface and vary off the line that uses the resource before it shows up in SST as being available to be used. After the lines are varied off, F13 lists the adapter and allows you to select that adapter. After you assign it to the STS LAN adapter and then store and activate, you can vary on the line that uses the same resource on the system and start the interface.
d) Press Enter.
e) Enter the TCP/IP information. Your network administrator needs to provide a valid and unique TCP/IP address that can be used for the service tools server for DST.
f) Press F7 (Store).
g) Press F14 (Activate).
Verify that an alternate installation device is not defined:
'Untag' or 'de-select' the alternate installation device on the client system before starting the network installation. Instructions to deselect that alternate installation device is found here: https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/i/7.5?topic=uaid-disabling-alternate-installation-device
On NFS Server:
To verify NFS is up and running properly, do the following:
WRKACTJOB SBS(QSYSWRK) JOB(QNFS*)
If you see the following active, all is good:
QNFSMNTD QUSER BCH .0 SELW <=== *Mnt
QNFSNFSD QUSER BCH .0 TIMW <=== *SRV
QNFSNFSD QUSER BCH .0 DEQW <=== *SRV
QNFSRPCD QUSER BCH .0 SELW <=== *RPC
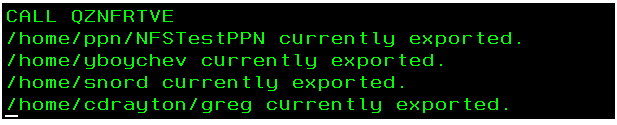
On the NFS Server partition, run 'CALL QZNFRTVE' to see which directories are exported.
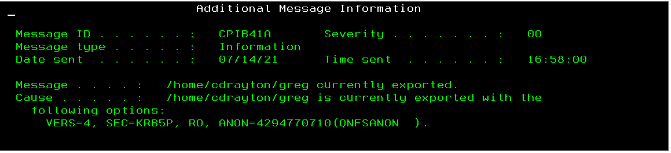
In the user's interactive job log, you can see something like this:
Related Information
Document Location
Worldwide
Was this topic helpful?
Document Information
Modified date:
16 December 2025
UID
ibm16967363