CSV file format for extended data sources
You can define extended data sources in a comma-separated value (CSV) file, which you can import into the catalog.
Purpose
Use a CSV file to import the following main types of extended data sources into the catalog: application, stored procedure definitions, and files. The CSV file uses specific syntax for each of these assets to create them in the catalog.
Templates and samples
From the Import Extended Data Sources pane (), download the compressed file that contains CSV files with samples of application, stored procedure definition, and file extended data sources. The samples have all sections and columns in the correct syntax for each asset. Modify these samples to suit your needs.
Syntax
Application, stored procedure definitions, and files have unique sections in the CSV file. Therefore, create separate CSV files for the general types that you want to import. To define an application, stored procedure definition, and file in the CSV file, follow these syntax rules.
- Sections
- The sections for application, stored procedure definition, and file define the context of each asset to import into the catalog.
- Columns and column headings
- The columns of all sections must be in this sequence:
- Name of the extended data source
A value in this field is required. If no name is listed, the row is ignored.
Do not use the following special characters in the name: , " [ ] '.
- Parents of the extended data source, if any exist
The sections Application, Stored Procedure Definition, and File do not have this column.
All other sections contain a column for each of its parent sections, according to its context. For example, the section for an input parameter asset has three columns for parents: application, object type, and method. The section for an in parameter asset has one column for its parent, stored procedure definition.
If no value is listed in a parent column or if the value does not match the extended data source type, the row is ignored. For example, in a section for a method, MyApp1 is in the Name column, the Object Type column is empty, and NewMethodTest is in the Method column. This row is ignored during import because a method must have a parent of object type.
- Description
A value in this field is optional. It is the last column of every section.
- Name of the extended data source
- Comments
- To include a comment in a row, insert an asterisk (*). The entire row is ignored during import.
- Put an asterisk only at the beginning of the row. Do not put comments within a row.
- You can include empty rows between sections to make the CSV file easier to read. You do not need an asterisk if the entire row is empty.
- Special characters and language support
- Commas
- If you create a CSV file instead of modifying a template, a comma (,) is the only accepted delimiter.
- Quotation marks
- Quotation marks (") are required if the value in a field includes non-alphanumeric characters such as mathematical symbols or commas. For example, the following value in the Description field must be enclosed within quotation marks because of the embedded commas: “This is the first, middle, and last description of the application.”
- Language support
- The CSV file must be in UTF-8 or in ANSI encoding to be compatible with all languages.
Example
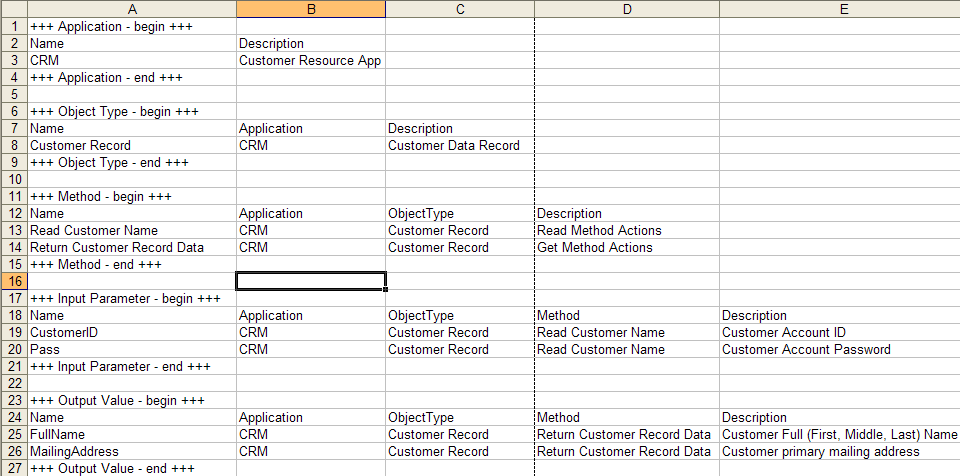
| Type of extended data source asset | Name of extended data source to be imported | Context of the extended data source to be imported |
|---|---|---|
| Application | CRM | |
| Object Type | CustomerRecord | CRM |
| Method | ReadCustomerName ReturnCustomerRecordData |
CRM.CustomerRecord CRM.CustomerRecord |
| Input Parameter | CustomerID | CRM.CustomerRecord.ReadCustomerName |
| Output Value | FullName | CRM.CustomerRecord.ReturnCustomerRecordData |