Layout of a Virtual Address Space
The address space layout that is shown (size >16 MB) applies also if the address space size is 16 MB, which is the required minimum.
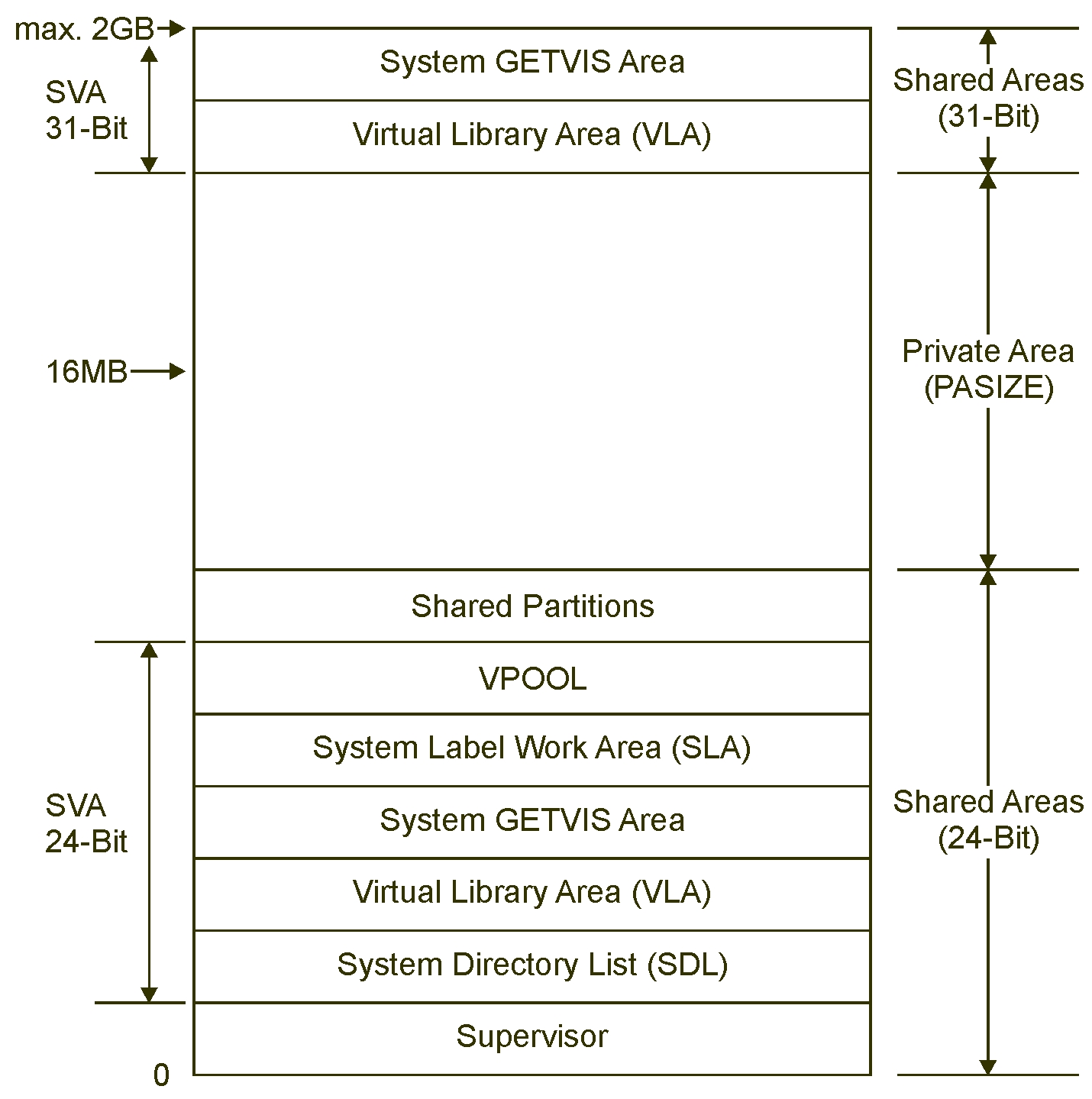
The possible maximum size of this address space is 2 GB. For a running system,
the actual size of an address space is to be calculated as follows:
PASIZE + size of shared areas 24-bit and 31-bitThe SVA (24-Bit) includes the following:
- The VPOOL area is needed to exchange data with the VIO (virtual I/O area).
- The SLA is the area that is used by z/VSE to store and maintain system and user label information.
- The system GETVIS area is an area of virtual storage that is reserved for use by the system.
- The VLA is the area in which phases resident in the SVA are stored.
- The SDL is the directory of the phases to be loaded into the SVA during system start.
The SVA (31-Bit) includes the following:
- The system GETVIS area is an area of virtual storage that is reserved for use by the system.
- The VLA is the area in which phases resident in the SVA are stored.
Note:
- The shared areas (31-Bit) can start below 16 MB, dependent on the PASIZE specification and the shared areas (24-Bit), and can cross the 16 MB line.
- SDL, SLA, VPOOL, and shared partitions are only available in the shared areas (24-Bit).
- The private area must start at least 1 MB below 16 MB.