Transporting data securely across a network
You may need to protect data that is sent between two applications when the data must pass through one or more intermediate systems.
In a DES cryptographic system, if the two applications cannot share a key, you must set up an application on one or more of the intermediate systems to translate the ciphertext from encryption under the sending system's key. Translation re-encrypts the ciphertext under a new key for which the receiving system has a complementary key.
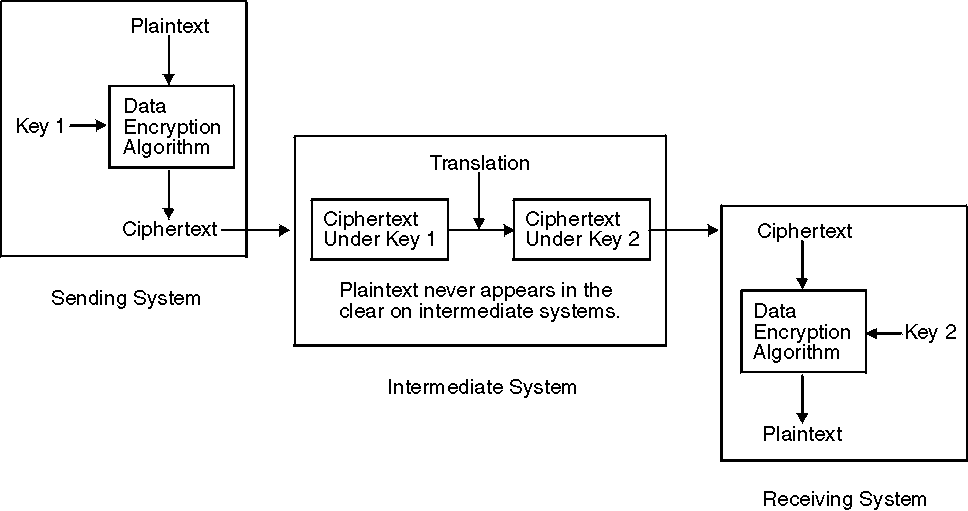
In a PKA cryptographic system, you can develop an application that does not require translation of ciphertext by the intermediate systems. The sender enciphers the message by using a DES or AES data-encrypting key. The sender then uses the receiver's PKA public key to encipher the DES or AES data-encrypting key. The intermediate system merely transfers the ciphertext and the enciphered key to the receiving system. The intermediate system does not have the receiver's PKA private key and, therefore, cannot decipher the enciphered data-encrypting key. Without the deciphered data-encrypting key, the intermediate system cannot decipher the message. The receiving system uses its PKA private key to decipher the DES or AES data-encrypting key, which it then uses to decipher the message Figure 2.
