Cluster configurations with multitiered applications
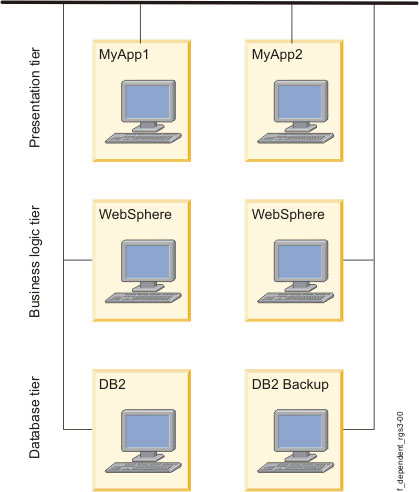
A typical cluster configuration that could utilize parent and child dependent resource groups is the environment in which an application such as WebSphere® depends on another application such as DB2®.
In order to satisfy business requirements, a cluster-wide parent and child dependency must be defined between two or more resource groups.
The following figure illustrates the business scenario that utilizes dependencies between applications:
Multitiered applications
Business configurations that use layered, or multitiered applications can also utilize dependent resource groups. For example, the back end database must be online before the application controller. In this case, if the database goes down and is moved to a different node, the resource group containing the application controller would have to be brought down and back up on any node in the cluster.
Environments such as SAP require applications to be cycled (stopped and restarted) anytime a database fails. An environment like SAP provides many application services, and the individual application components often need to be controlled in a specific order.
Another area where establishing interdependencies between resource groups proves useful is when system services are required to support application environments. Services such as cron jobs for pruning log files or initiating backups need to move from node to node along with an application, but are typically not initiated until the application is established. These services can be built into application controller start and stop scripts. When greater granularity is needed, they can be controlled through pre- and post- event processing. Parent/child dependent resource groups allow an easier way to configure system services to be dependent upon applications they serve.